Calculate voltage division across multiple resistors. Results include node voltages, current flow, and power dissipation.
A voltage divider, also known as a potential divider or voltage splitter, is a simple passive linear circuit that produces an output voltage () that is a fraction of its input voltage ().
The core of a voltage divider is the use of two or more resistors connected in series. As current flows through these resistors, a voltage drop occurs across each resistor based on its resistance value. The voltage is divided proportionally between the resistors.
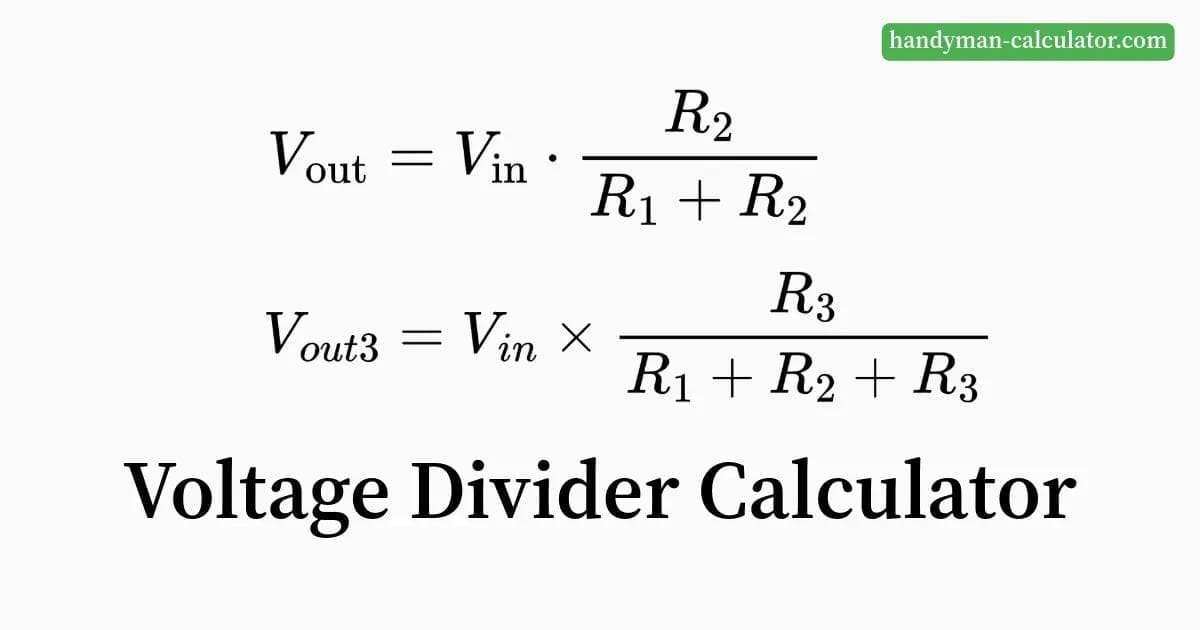
This is the simplest and most common configuration, using two resistors ( and ) connected in series to an input voltage.
Circuit Description:
Input voltage () is applied across both resistors. The output voltage () is measured across .
Formula: The output voltage is calculated as follows:
Where:
Input voltage () = 12V, :
Output voltage () = 4V.
A 3-resistor divider provides more flexibility and uses three resistors connected in series.
Circuit Description:
Input voltage () is applied across all three resistors (). The output voltage () can be measured across or between and .
Formulas:
Output voltage across :
Output voltage between and :
Example:
Input voltage () = 15V, :
Output voltage across = 7.5V.
Voltage dividers are ideal for scaling sensor outputs. For long-distance sensor wiring, prevent power loss with our Voltage Drop Calculator.
No, voltage dividers are not suitable for powering devices with significant current requirements. For such cases, use voltage regulators.
The resistor values depend on your application: * Higher resistances minimize power loss but are more susceptible to noise. * Lower resistances provide better stability but increase power consumption.
Voltage dividers are essential building blocks in electronics. By understanding their principles and using our online calculator, you can design circuits to achieve desired voltage levels. Whether for sensor applications, voltage reduction, or signal conditioning, a good grasp of voltage dividers is invaluable. Experiment and keep designing!